
Tuna has always been a staple Real Food in our home. I’ve always taken care to source low mercury, sustainably caught tuna in order to prepare quality tuna steaks for dinner, tuna melts for lunch, or that old standby tuna salad for lunch boxes, quick snacks or just a dollop on a bed of greens. Spicy bluefin tuna rolls are a favorite of my husband when dining at Japanese restaurants.
About a year ago, however, I started to question my choice of tuna for regular consumption. I began reading the reports about the spreading radiation plume in the Pacific from the continuing Fukushima nuclear disaster. I delved into the migratory patterns of various species of tuna. The more I read, the more concerned, and quite frankly, confused I became.
Realizing that my family’s health can’t be wagered on guesses or half-truths, I gathered as much information as I could to arrive at an informed decision. Here’s what I found.
All species of tuna are highly migratory. This means that they swim long distances pretty much throughout their entire lives. These migration patterns are still ill-understood although it is generally agreed upon that they are large.
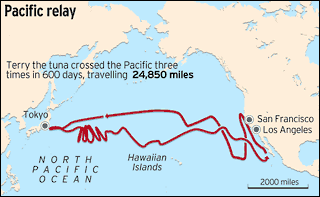
Pacific bluefin tuna are born near Japan spending their early months swimming in the radiation plume there. They then swim back and forth across the Pacific their entire lives. One tuna nicknamed Terry crossed the Pacific no less than 3 times in the span of only 20 months coming very close to Japan each time. To the right is a chart showing his epic swim.
The information gleaned from Terry the tuna is not new. As early as the 1950’s, tagged albacore tuna were known to swim thousands of miles as shown in this second chart to the right. The open circles off the California coast indicate where they were released and the solid circles closer to Japan indicates where they were recaptured.
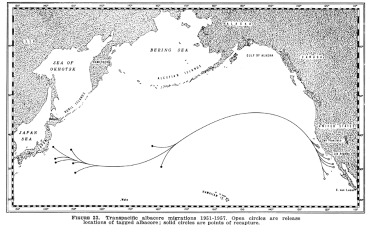 Highly migratory indeed!
Highly migratory indeed!
Atlantic based tuna exhibit the same nomadic patterns. According to National Geographic, high tech tags of Atlantic bluefin tuna revealed the following:
A team of international scientists documented two giant bluefins tagged within minutes of each other off the coast of Ireland. The two fish swam to opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean–ending up more than 3,000 miles (5,000 kilometers) apart. One of the fish traveled 3,730 miles (6,000 kilometers) southwest to waters about 186 miles (300 kilometers) northeast of Cuba. The other remained in the eastern Atlantic and moved off the coasts of Portugal.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation (FAO)s, all species of tuna, not just bluefin and albacore, are considered highly migratory, again with the reasons for these patterns not well understood. Here is a breakdown of the tuna species and where they are located according to a report by the FAO:
- Albacore tuna (Thunnus alalunga), which occurs in tropical and temperate waters worldwide.
- Bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus), mostly found in temperate waters of the Atlantic, including the Mediterranean, and Pacific Oceans. It is noted that since the adoption of UNCLOS, bluefin tuna in the northern Pacific has been identified as a different species, Pacific bluefin tuna (Thunnus orientalis) while bluefin in the Atlantic has been re-named Atlantic bluefin tuna.
- Bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus), found in the Atlantic (but absent from the Mediterranean), Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Skipjack tuna (Katsuwonus pelamis) with a worldwide distribution in tropical and temperate waters.
- Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares), also with a worldwide distribution in tropical and sub-tropical more temperate seas, but absent from the Mediterranean.
- Blackfin tuna (Thunnus atlanticus) found in the western Atlantic in tropical and warm seas.
- Little tuna (Euthynnus alleteratus and E. affinis), with E. alleteratus found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Atlantic, including the Mediterranean, the Black Sea, the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, and E. affinis in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is noted that presently, E. alleteratus is called little tunny and E. affinis is called kawakawa.
- Southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii), in temperate waters of the southern hemisphere in the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Oceans.
- Frigate and bullet tuna (Auxis thazard and A. rochei) found in the Atlantic (including the Mediterranean Sea where only A. rochei is found), Indian and Pacific Oceans.
So Tuna Swim. A Lot. So What?
The fact that tuna swim great distances, constantly moving and migrating means that tuna in the Pacific more than likely will have passed through the growing Fukushima radiation plume at some point in their lives, probably numerous times.
With long-lived varieties like albacore (11-12 years) and bluefin (up to 20 years), this is especially true. With much smaller, shorter-lived tuna like the skipjack (about 8 years), less so.
Is the Fukushima Radiation Even Really a Problem?
The answer to this question depends on who you ask. Some reports say yes, the Pacific-based radiation plume from Fukushima is a serious problem and growing worse as 300 tons of radioactive water pours into the Pacific every single day with no end in sight for years. Unbelievably, Japan’s government only acknowledged the urgency of the situation in September 2013.
On the other hand, a comprehensive assessment by the World Health Organization (WHO) concluded that radioactive particles that are making their way to North American waters will have a limited effect on human health, with concentrations below WHO safety levels.
The most unsettling data to date is that the continued outflow of radioactive water from Fukushima now no longer just contains cesium isotopes. It now also contains the more worrisome strontium-90 which is a bone-seeking isotope.
Who is right? Who is wrong?
One thing is true, Fukushima is a nuclear disaster never before experienced in human history so all theories and probabilities are on the table.
Dr. Ken Buessler, a world expert in marine radioactivity with the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution in Massachusetts who is leading an international research team tracking Fukushima’s trails in the Pacific has this to say:
We still don’t know the answers to many important questions concerning the impacts of Fukushima radionuclides on the oceans. For example, we still don’t have a good handle on how much radioactivity was released, and we don’t fully understand where it has ended up, and that holds for the ocean waters, seafloor sediments, and for marine biota, such as tuna.
Caution Seems to Be the Best Policy
Having personally known someone who died of radiation-induced cancer 15 years after the Chernobyl disaster from the fallout that blanketed parts of Europe which governments at the time said was no threat to human health (his wife lost most of her hair but has survived although they tragically had a daughter born a few years after the disaster who developed leukemia), I don’t take the long term, cumulative effects of radiation lightly and interpret official reports like the one published by the WHO with a grain of salt.
If you choose to interpret the data as a nonthreat to human health with the radiation levels within safe limits, that is, of course, your choice. My approach is both practical and cautionary to play it safe for my children’s sake until more information is gathered and the extent of the problem studied further. This includes avoiding all tuna from Pacific waters given that this particular migratory fish is prone to swimming close to Japan multiple times during its lifetime.
Since much of the time, the ocean of origin for tuna is unknown or not labeled, this would mean avoiding all tuna in most cases. This is exactly what I’ve been doing for the past six months or so – no tuna in my home. Period.
The complaining of my family about the absence of tuna dishes (which everyone loves) has caused me to continue to search for a source of tuna I would feel comfortable serving. I recently discovered a skipjack tuna from Portugal (source) that I’ve been purchasing for several years.
Buy Atlantic Based Tuna!
Given that Atlantic based tuna do not enter the Pacific during their lives, I felt at this time, this brand of sustainably-fished Atlantic tuna would be safe to eat.
However, predictions are for the Fukushima radiation plume to continue growing, eventually entering the Arctic and then the Atlantic Oceans, as the disaster is far from contained. As a result, this situation most likely will change in the coming years. For now, however, if tuna origin can be accurately confirmed, I will purchase and eat it – but only from the Atlantic Ocean and other non-Pacific sources.
What are your thoughts about eating tuna and other seafood? What data have you come across to support your decision? Do you continue to eat tuna? Why or why not?

References
(1) Radiation From Fukushima Could Help Solve the Mystery of Bluefin Tuna Migration
(2) Health risk assessment from the nuclear accident after the 2011 Great East Japan earthquake and tsunami, based on a preliminary dose estimation
(3) Tagged Tuna Reveal Migration Secrets
(4) Tuna’s 25,000 Mile Swim Down Marine Highway
(5) The Migration, Age, and Growth of Pacific Albacore (1951-1958)
(6) Should you Worry about Radiation in your Wild Pacific Fish?
(7) Highly Migratory Species of Fish
(8) Tuna Species








Thanks, Jocelyn. I’ve been avoiding tuna because of the mercury, Colin’s been avoiding it since he got sick on Subway’s tuna, but our son-in-law loves sushi, and we love him, and I hadn’t even considered the threat of radiation!
Radiation may be harmful to Tuna. Being caught and served for dinner is also harmful to tuna. But there isn’t any particular mechanism I can think of where the radiation that the Tuna may be exposed to actually affects the people who eat the meat at some point later. Radioactivity is scary, but it isn’t magical.
I stocked up on canned tuna a while ago when it was on sale. I don’t just want to throw it all away unless necessary. How can I tell when it was packaged to get an idea if it was canned before the disaster? Or is there any other way to get an idea for whether it is safe to eat?
Thank you for the information.
I avoided tuna long before the Fukushima disaster, since it’s very high in mercury. Sadly, it’s hard to find non-contaminated seafood these days.
not very eco-concious of you to be consuming a fish that has been overfished to just 20% of their population just 40 years ago…and all you care about radiation is going to affect you? Fukushima may be the best thing to happen to the ocean’s wildlife…
Waterways poisoned by industry is not a new issue…if they don’t poison them directly (ie. factories next to large bodies of water) they poison them through other environmental sources, mainly air pollution.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Minamata_disease
Bravo! For making a hard decision. When most people are towing a political line and others are just believing the government is protecting them, while they fall prey to the ridiculous consumption limits set by agencies that Do NOT have their best interest in mind…But do have the interest of Big Business in mind and the avoidance of crippling an entire industry….
Of all the foods with problems today, and this is not a short list, poisoning of the oceans, rivers and waterways has for YEARS made ALL foods from these sources unsafe for consumption – sorry folks this was even true well BEFORE the Fukushima issues. For those who think it is just Pacific Coast/Fukushima tainted foods, wake-up, no such luck! Sorry. xo
Thank you so much for this article!!!
Thanks for the in depth research, think i will continue avoiding tuna.